-
 Tail Light 1 x $80.00
Tail Light 1 x $80.00 -
 Wiper Blades 1 x $80.00
Wiper Blades 1 x $80.00 -
 Suspension 1 x $80.00
Suspension 1 x $80.00 -
 Air Filter 1 x $80.00
Air Filter 1 x $80.00 -
 Car Brakes 1 x $80.00
Car Brakes 1 x $80.00
Overview
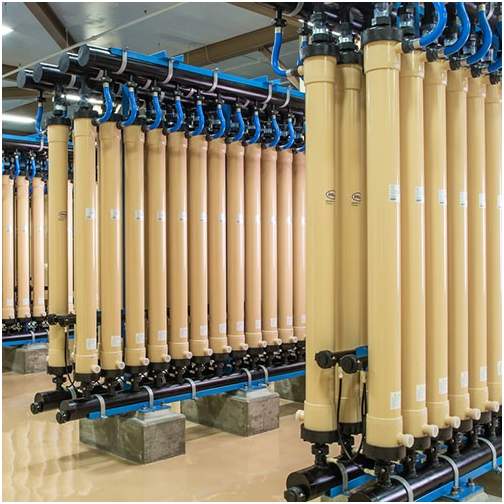
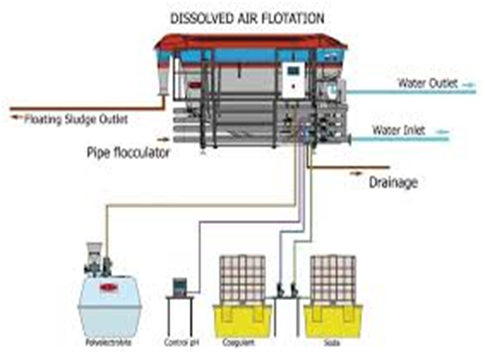
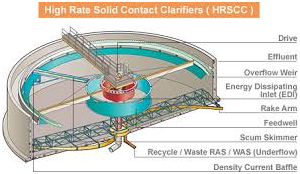
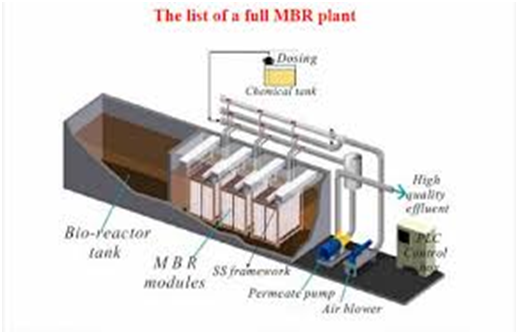
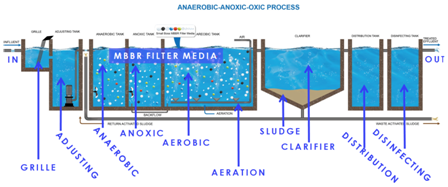
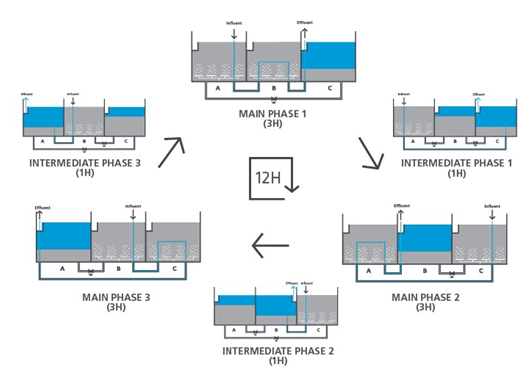
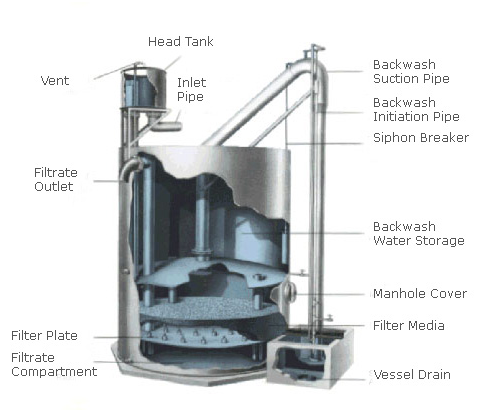
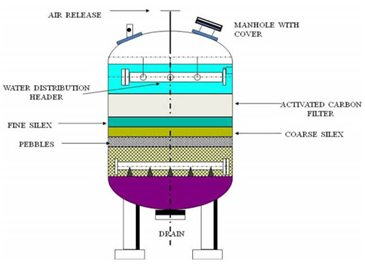
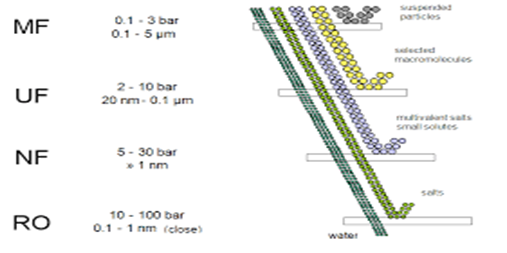
The need for wastewater treatment systems is mandatory for all industries now. You have to make your industry PCB pollution norms compliant to be able to operate.
Wastewater is any water that requires cleaning after it is used. The goal of wastewater management is to clean and protect water. … This means that water must be clean enough so that it can be used by people for drinking and washing, and by industry for commercial purposes.